Introduction
Technical textiles can be utilized alone or in combination with other products. Technical textiles, such as coated fabric for awnings and fire retardant fabric for firefighter uniforms, are employed separately to fulfill certain purposes. They are utilized as a component or part of another product to improve its performance, strength, or other functional qualities.
A number of factors, including functional requirements, health and safety, cost effectiveness, durability, high strength, lightweight, versatility, customization, user-friendliness, eco-friendliness, logistical convenience, etc., have contributed to the gradual but steady rise in the popularity of technical textiles. Technical textiles are utilized primarily because of their unique physical and functional characteristics, as opposed to ordinary ones, which are typically used for clothing or furnishings.
What are technical textiles?
Technical textiles are defined as textile materials and products used primarily for their technical performance and functional properties rather than their aesthetic or decorative characteristics. Technical textiles are also referred to as industrial, functional, performance, engineering, invisible and hi-tech textiles.
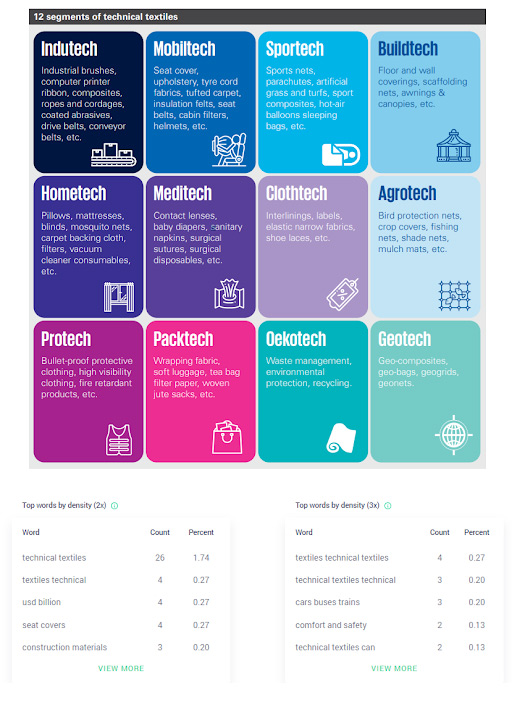
Technical textiles are grouped into various segments depending on the product characteristics, functional requirements and end-use applications. Currently, technical textile materials are most widely used in filter clothing, furniture, hygiene medicals and construction materials.
Classification and Application of Technical Textiles
Technical textiles can be divided into many categories, depending on their end-use. The classification system developed by Techtextil, Messe Frankfurt Exhibition GmbH, is widely used in Europe, North America, and Asia.
AGROTECH (AGRO-TEXTILES)
Agrotech are specialized fabrics used across various industries, including food production, fishing, and agriculture. These technical textiles include bird protection nets, plant nets, monofilament nets, root ball nets, insect protection nets, weed control fabrics, and fruit covers. Agrotech technical textiles have features such as durability and flexibility, that protect from environmental dangers, support plant growth and safeguard crops from pests, birds, and harsh weather. It also helps in improving micro-climates, reducing the need for pesticides, and promoting sustainability in agricultural practices.
BUILDTECH (CONSTRUCTION TEXTILES)
The growing landscape of technical textiles technology has brought about significant shifts in various sectors. One such is building construction materials, where the technical fabrics are chosen for their features like strength-to-weight ratio, durability, flexibility, insulation, and fire resistance. These are increasingly replacing traditional materials such as steel, wood, and plastics in construction projects. Some examples of these innovative textile-based construction materials include:
- Textile-Reinforced Concrete: This is a form of concrete enhanced with textile fibers that improve its strength and durability.
- Fiber-based Bridging Cables and Elements: Usually incorporated in modern bridge construction, they offer strength without the weight of traditional materials.
- Erosion and Landslide Protection Systems: Materials are employed to reinforce areas that are susceptible to erosion or landslides, offering a lightweight solution.
- Water Management Systems: Used in reinforcing dykes and other structures to manage water, by providing a durable, cost-effective alternative.
- Flexible, Lightweight Piping and Canalization: Textile-based pipes are being used for their durability and ability to withstand environmental stresses.
HOMETECH (HOME-TEXTILES)
For a long time, home textiles have been used in the interiors of homes and transportation systems such as cars, buses, trains, cruise ships, and aeroplanes. Traditionally, they served three primary functions decoration, comfort, and safety. With the recent shift in the industry, the increasing demand for these goes beyond mere aesthetic or comfort purposes to meet practical and safety needs.
Enhanced Functionality and Applications
- Stain or Water Repellence: This is utilized in tablecloths, curtains, furniture, and seat covers for vehicles like cars, buses, trains, and airplanes to maintain cleanliness and durability.
- Flame Retardance: Ensures safety in case of fire for all types of textile interiors, both in buildings and transportation systems.
- Anti-static Properties: Upholstery and seat covers benefit from anti-static materials to reduce static electricity, giving both comfort and safety.
- Anti-bacterial Properties: These help to maintain hygiene by preventing bacterial growth in bedding and medical textile.
- UV Protection: It is used in roofing, tents, awnings, blinds, and curtains to protect against harmful ultraviolet rays.
Odor Absorption: To be utilized in bedding, furniture, and seats in cars, buses, trains, and aeroplanes to ensure a more pleasant environment.
GEOTECH (GEOTEXTILES)
Geotextiles are used in civil engineering projects for support, drainage, separation, reinforcement, and protection. Geo- technical textiles have recently gained popularity for waste management, particularly in facilities that handle municipal and industrial wastewater and at hazardous waste sites.
They aid in preventing erosion, help to stabilize unstable soils, and enable regulated water flow to improve soil texture. They are also being utilized more and more in waste management to treat effluent and contain hazardous material, protecting the environment.
CLOTHTECH (CLOTHING TEXTILES)
Clothing textiles include a variety of materials that contribute to the overall functionality and durability of garments. Sewing threads, shoe laces, interlining, and zip fasteners are a few examples that help enhance the structure, comfort, and usability of clothing. Clothing fabrics play an integral role in the design, performance, and longevity of modern clothing, meeting the demands of both fashion and functionality.
INDUTECH (INDUSTRIAL-TEXTILES)
From filtration and cleaning to material transportation and machine operation, technical textiles are essential to many industrial processes. They transport materials through processes, clean gasses and effluents, and separate and purify products.
Key applications include:
- Used in purifying industrial products, cleaning gases, and effluents.
- Conveyor belts and ropes are used to move materials through production processes.
- For machine operations, they are used in drive belts and abrasives.
- Other applications include products like decatising cloth, bolting cloth, coated abrasives, and knitted nets.
- Filtration and cleaning products remain among the most important segments of technical textiles, ensuring efficiency and environmental safety in industrial operations.
MEDITECH (MEDICAL TEXTILES)
The softness, flexibility, and absorption qualities of textile materials make them ideal for use in healthcare and hygiene. Traditional applications include medical bedding, braces, diapers, and wound care. Here are a few examples of how medical technical textiles are being used to improve patient care and recovery.
- Textile-Based Implants: Replacing donor organs with textile implants and artificial tissues.
- Recovery Aids: Breathable wound dressings and lightweight, comfortable prosthetics.
- Quality of Life: To ease chronic illness and make the care provision more scaleable, functional clothing is used; for instance in rehabilitation equipment for surgeries or chronic illnesses. These innovations not only improve treatment outcomes but also help reduce medical costs.
PROTECH (PROTECTIVE TEXTILES)
Protective technical textiles are designed to provide safety in hazardous environments. These textiles include a wide range of garments, from industrial gloves to high-visibility clothing, each engineered for specific protective functions. Some are designed to shield the body from physical hazards like cuts, abrasions, and impacts, while others protect against extreme temperatures, flames, or chemical exposure. Additionally, protective fabrics include advanced materials that enhance safety and security to provide life-saving protection against ballistic threats. These textiles combine durability, functionality, and innovation to meet the demands of high-risk work environments.
SPORTECH (SPORTS TEXTILES)
Sporting products and equipment have seen the increasing usage of sports materials like specialized fibers, sportswear, and high-performance composites like boats, amongst other applications.
Key areas include:
- Sportswear: High-performance technical fabrics for better safety and comfort.
- Outdoor Gear: Tents, boat covers, and other leisure equipment.
MOBILTECH (AUTOMOTIVE TEXTILES)
Mobiltech, or automotive fabrics, encompasses a range of specialized materials used across various components in the automotive and transportation industries. These technical textiles are used in tyres, seat belts, airbags, seat covers, helmets, and airline seat covers and are designed with precision. They combine strength, durability, and comfort to meet the unique requirements of each of its applications. By continuously advancing these materials, the automotive industry promises safety, performance, and overall functionality, and ensures a more reliable and comfortable experience for passengers and users alike.
PACKTECH (PACKAGING TEXTILES)
Packaging textiles are materials used to protect and store products during transportation and storage. These technical textiles, like woven bags, fabric wraps, and sacks, are strong, durable, and versatile to bear and beat the rough transit journey. They provide an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional packaging options. These technical textiles help keep products safe and secure due to their moisture and heat resistance. As sustainability becomes more important, these textiles are gaining popularity because they’re reusable and have less environmental impact compared to other packaging materials.
Concluding thoughts
India’s technical textiles trade has seen significant growth, with the country becoming a net exporter. Exports of technical textile products surged from USD 2.21 billion in 2020-21 to USD 2.85 billion in 2021-22, marking a year-on-year growth of 28.4%. On the other hand, imports increased from USD 1.7 billion to USD 2.46 billion, reflecting a growth of 44% year-on-year.
The future of India with technical textiles looks promising, as these innovative materials continue to drive advancements across various industries, from healthcare to automotive. With a growing focus on sustainability and technological innovation, technical textiles are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping India’s economic and industrial landscape. To maintain sustainable growth and improve the overall competitiveness of the industry, there is a need for innovation, domestic production of specialty fibers, and a focus on reducing reliance on imports for technical textiles.